A changing climate will affect the risk profile of climate-related events in society. A warmer climate will lead to more extreme weather events, which in turn will affect us and our surroundings. These physical climate risks are the consequences of, for example, rising sea levels and increased occurrence of extreme weather with torrential rain, resulting in floods and landslides. Climate-related risks lead to financial risks and increased financial stress for banks, insurance companies and the real estate sector, among others.
To understand how these risks will affect our society, we can use geographic information to calculate where these risks are greatest and what their impact will be if an event occurs in an area with a designated risk.
- Knowledge and management of physical climate risks has therefore become an increasingly important issue and we are likely to see increased requirements for identifying and managing physical climate risks, not least linked to insurance and financing of assets," says Martin Hising, Product Manager Business Information at Metria.
- By combining analyzed data for identified climate risks with other types of real estate or business information, such as housing valuations and company data, the business not only gets a picture of the exposure to climate risks but also the financial impact on the business in case of materialized climate risk.
Data on climate aspects needed for banks' credit decisions
To understand how climate-related risks affect our society, we can use geographic information to calculate where the risks are greatest, analyze their impact and calculate the financial risk. In order for banks to base their credit decisions also on climate aspects, a large amount of data needs to be collected and analyzed.
Impact analysis forms the basis for planning and decision-making
By using designated risk factors, we can collect mapped risks together with information on which properties or activities are located in these risk areas. The analysis of what is affected can then form the basis for planning and decision-making and add statistical information to reports in, for example, climate and vulnerability analyses.
- Analyses of this kind can be handled at different geographical levels, ranging from looking at how an individual property or a portfolio is affected by a climate-related risk to how exposed a municipality is to climate-related risks, says Michael Ledwith, Senior GIS and remote sensing consultant and expert in flood analysis at Metria.
Integrating climate risk analysis into operations ensures sustainable lending
Taking climate-related risks into account and integrating them into credit and risk assessments secures financing and facilitates the business community's climate transition. The European Central Bank's stress tests show that banks need to integrate climate-related risks and opportunities more systematically into their operations and assessments. This requires data and expertise, something that we at Metria can help with.
At Metria, we collect information on several different types of risks to get an overall picture of the risk situation in a given area.
- In addition to existing maps, remote sensing and satellite data are powerful tools for mapping climate-related events. With up-to-date information, we can map the actual extent of an event and its impact at a given time. By aggregating risks into one analysis, we can put the analysis together and dress it up with, for example, valuation data or other business information to give a value of the area affected," explains Michael.
- "Once risks or events affecting our environment are identified, you can take the analysis a step further to see what actions you can take to climate-proof society. You can then model how such an implemented measure can reduce the risk and thus its potential impact," says Michael.
Flooding an identified risk in a changing climate
Flooding in communities can be caused by both precipitation and high river flows or torrential rainfall. A low point with a surface where water cannot infiltrate into the ground, such as asphalt, tends to fill with water during heavy rainfall, a so-called bluespot. In the long term, sea level rise can also cause coastal flooding.
Our collaborations in the analysis of climate-related risks
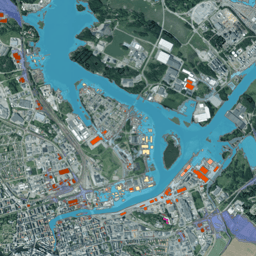
On behalf of MSB, Metria has produced a flood map of parts of Sweden, where we have analyzed the major cities along the coast as well as Jönköping and Karlstad. A study that identifies properties and/or buildings that would be affected by different types of floods. The mapping is based, among other things, on laser scanning and elevation data with data from aircraft and in some cases also processing of satellite data. The analysis covers cities in Sweden identified as risk areas in the Flood Ordinance, which includes priority areas around rivers, coastal flooding and lakes.
FACTS
Metria climate analysis for properties and homes in Sweden
With geographical information, we can calculate where the risks are greatest and how these areas will be affected by events such as storms or floods.
With the industry's sharpest minds, advanced data models and AI technology, we can, for example, accurately predict which buildings on a property are most exposed to climate-related risks.